Visiting Information
| Information | Details |
|---|---|
| Chinese Name | 东海大桥 (Dōnghǎi Dàqiáo) |
| Location and Address | Connects Shanghai’s Luchao Port in Nanhui District to Yangshan Deep-Water Port in Zhejiang Province |
| Opening Time/Hours | Open 24/7 for traffic |
| Entrance Fee | No entrance fee for vehicles using the bridge |
| How to Get There | By Car: Take S2 Expressway from Shanghai By Bus: Long-distance buses from Shanghai to Yangshan Port Note: No metro access available |
| Best Time for Visit | Year-round, but spring and autumn offer the best weather conditions |
| Contact Info | Not applicable (public infrastructure) |
Overview
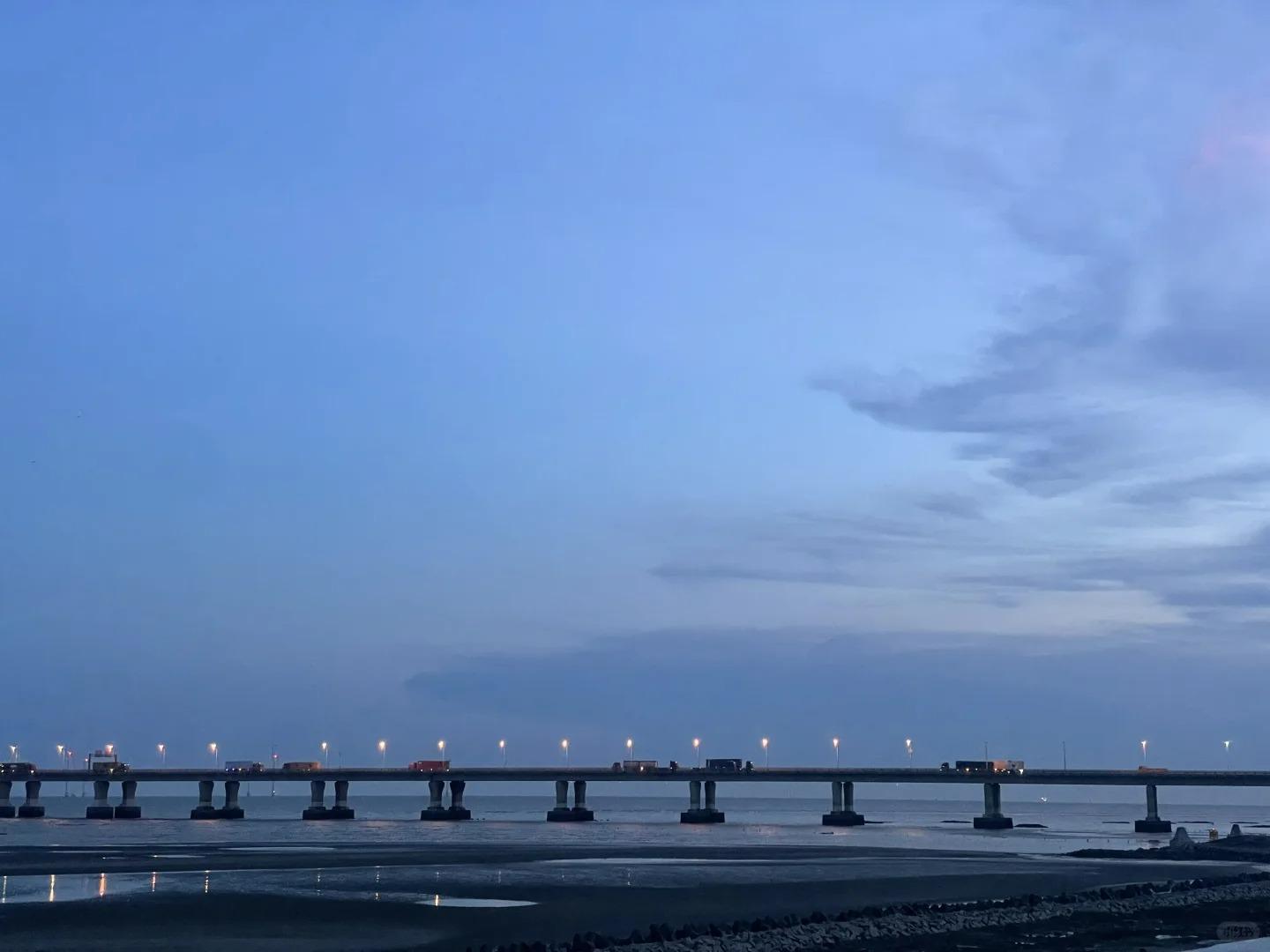
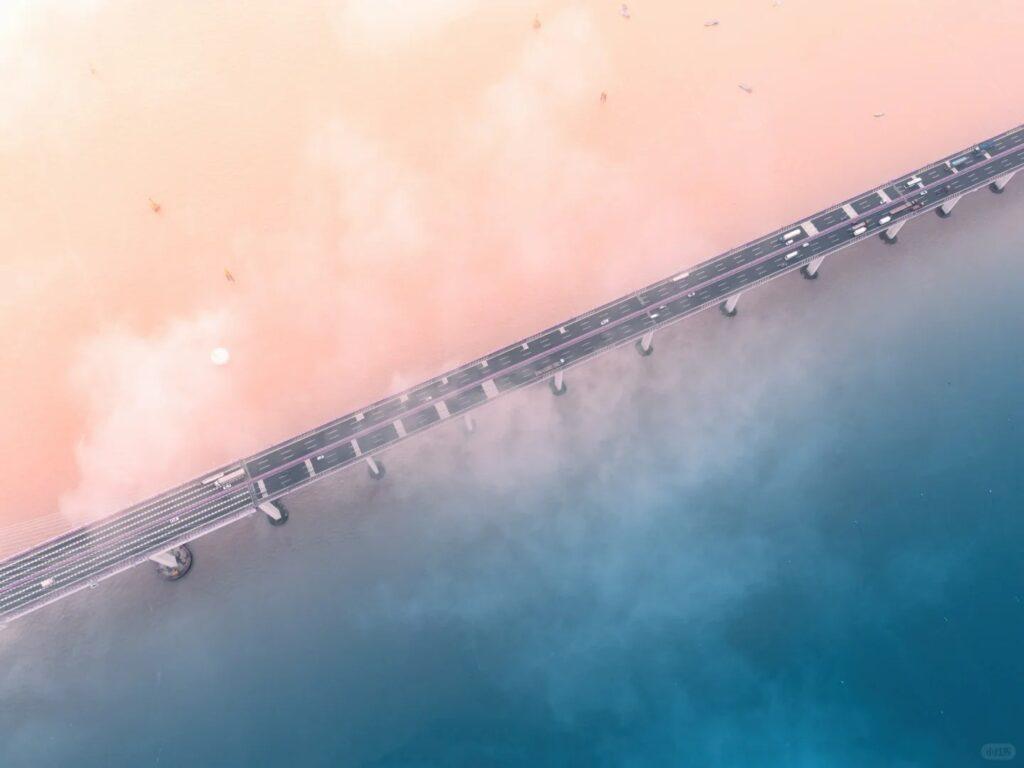
Donghai Bridge, also known as the East Sea Bridge, is one of the longest cross-sea bridges in the world. It spans 32.5 kilometers (20.2 miles) across the East China Sea, connecting Shanghai to the offshore Yangshan Deep-Water Port. The bridge is a crucial part of China’s infrastructure, facilitating trade and transportation in the region.
Historical Background
Construction of Donghai Bridge began in June 2002 and was completed in December 2005. The bridge was officially opened to traffic on December 1, 2005. It was built as part of the Shanghai Yangshan Deep-Water Port project, which aimed to expand Shanghai’s shipping capabilities and solidify its position as one of the world’s busiest ports. The bridge’s construction was a significant engineering feat, overcoming challenges posed by the region’s frequent typhoons and complex marine environment.
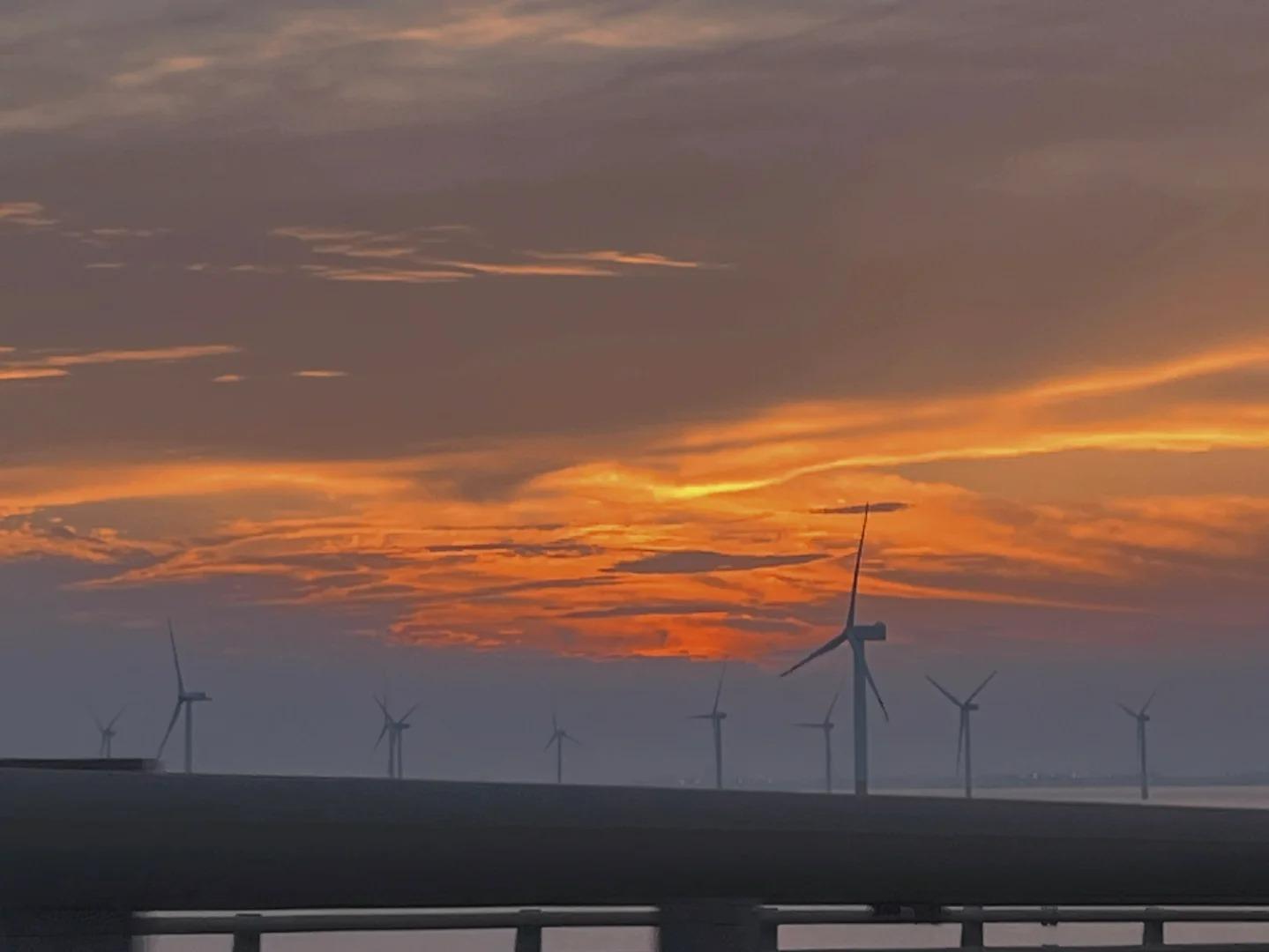

Architectural Features
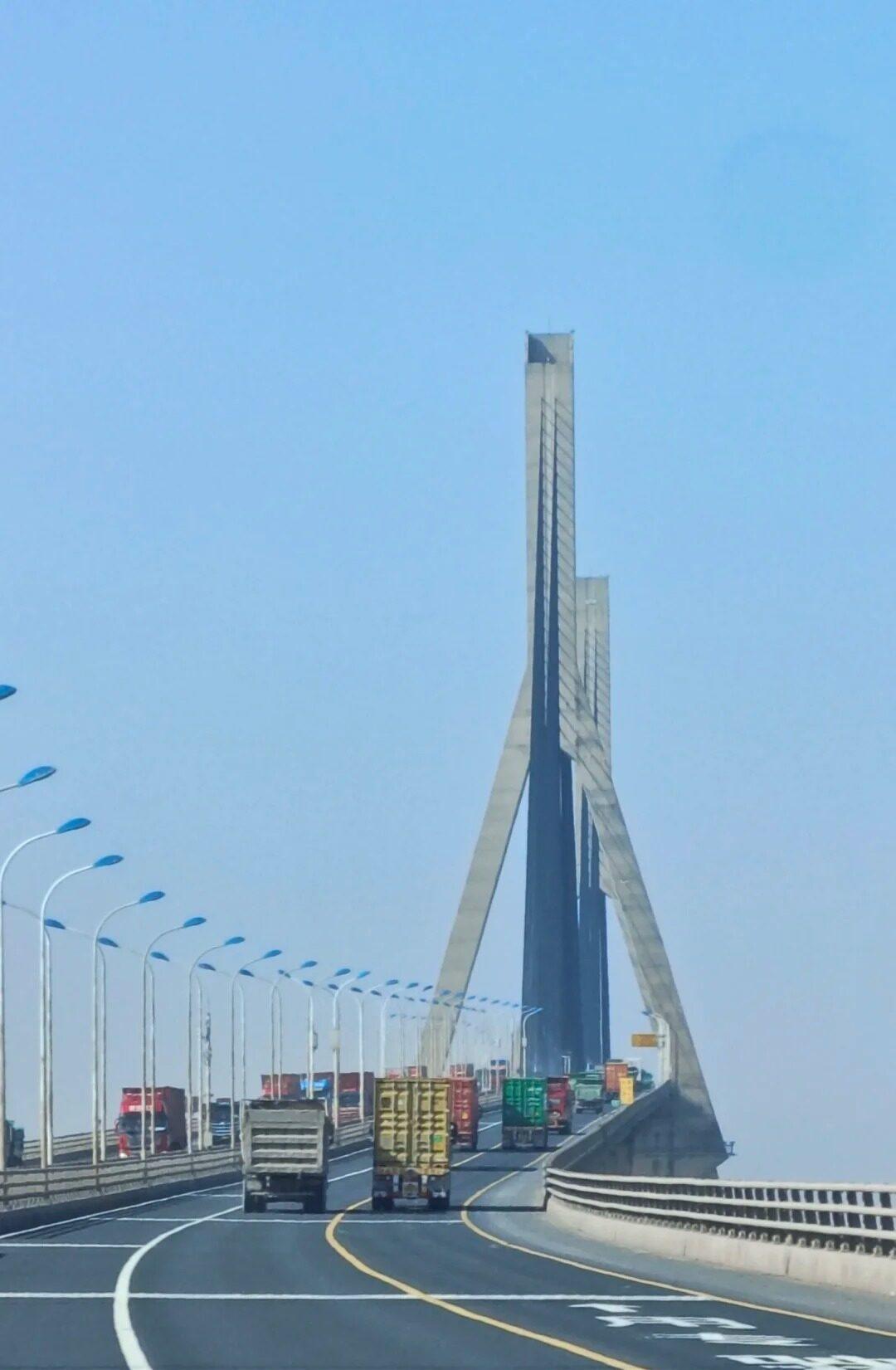
- Length and Structure: Donghai Bridge stretches for 32.5 kilometers, with the main bridge section measuring 25.3 kilometers. It consists of three cable-stayed spans and a long viaduct approach. The bridge is designed to withstand typhoons, high winds, and potential ship collisions, showcasing advanced engineering techniques.
- Pillars and Foundation: The bridge is supported by 1,400 foundation pillars, each driven deep into the seabed. These pillars are designed to withstand the harsh marine environment and provide stability to the structure. The deepest pillar reaches 80 meters below sea level, demonstrating the engineering challenges overcome during construction.
- Traffic Capacity: The bridge features a six-lane expressway, capable of handling significant traffic volumes. It’s designed to accommodate large container trucks and other heavy vehicles, playing a crucial role in the transportation of goods to and from the Yangshan Deep-Water Port.
- Navigation Channels: The bridge incorporates two navigation channels for ships to pass under. The main channel has a clearance of 40 meters, allowing large container ships to navigate safely beneath the bridge, ensuring that the structure doesn’t impede maritime traffic.
Cultural Importance
Donghai Bridge symbolizes China’s rapid economic development and its ambition to become a global leader in infrastructure and trade. It represents the country’s ability to undertake and complete large-scale engineering projects. The bridge has become an icon of modern China, often featured in documentaries and educational materials about engineering marvels. Its construction and operation have significantly contributed to Shanghai’s status as a world-class port city and have boosted regional economic development.
Surrounding Attractions
- Yangshan Deep-Water Port: At the eastern end of Donghai Bridge lies the Yangshan Deep-Water Port, one of the world’s busiest container ports. Visitors can observe massive container ships and state-of-the-art port facilities, gaining insight into global trade operations. The port area also offers a unique perspective on the scale of modern maritime commerce.
- Nanhui New City: Located near the mainland end of the bridge, Nanhui New City (now part of the Pudong New Area) is a rapidly developing urban area. It features modern architecture, eco-friendly design, and showcases Shanghai’s urban planning initiatives. Visitors can explore parks, lakes, and observe the integration of nature with urban development.
- Dishui Lake: This artificial lake in Nanhui New City is the largest man-made lake in Shanghai. It offers recreational activities such as boating and fishing, and is surrounded by parks and walking trails. The lake area provides a relaxing contrast to the industrial nature of the nearby port.
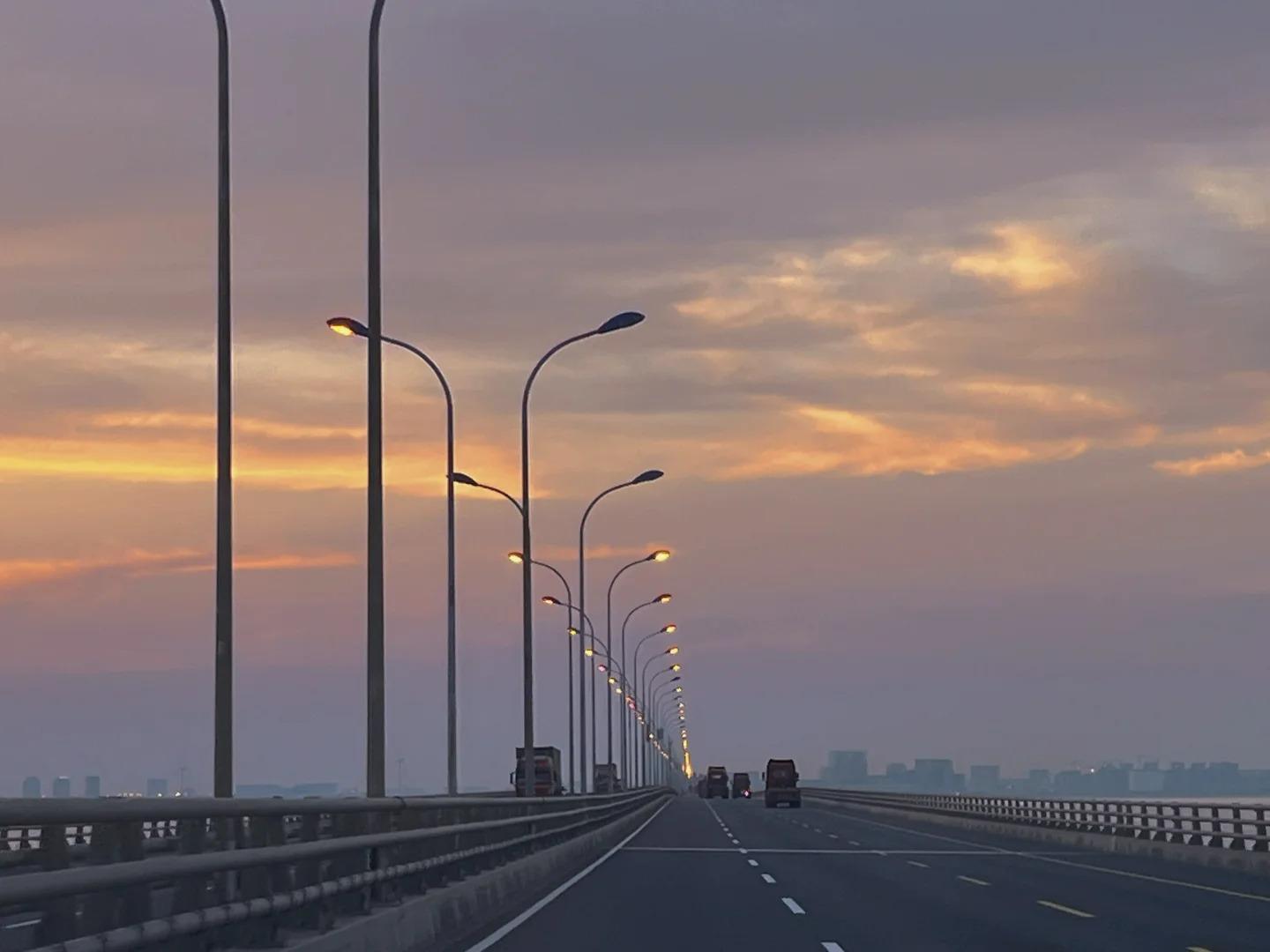

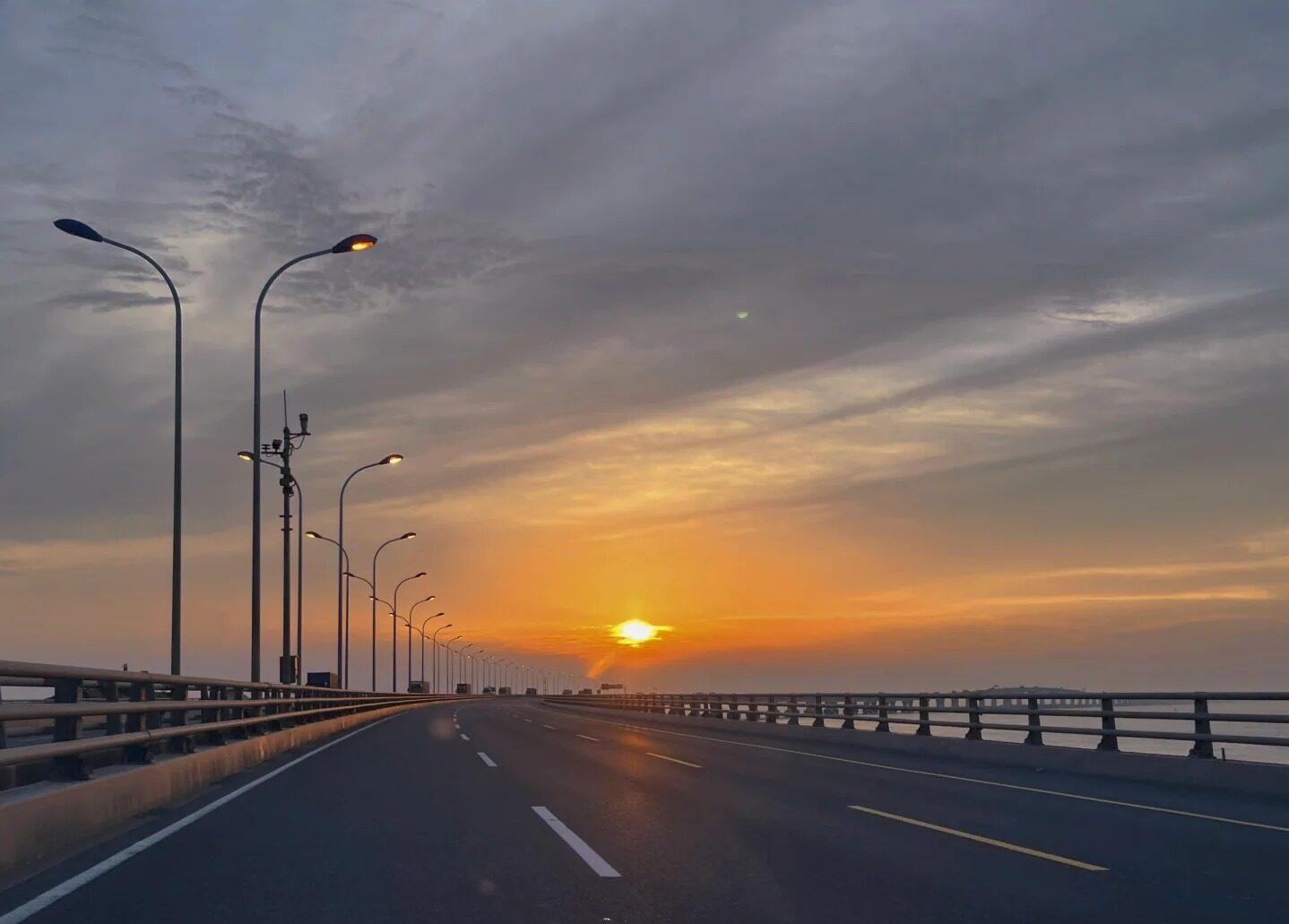
Photography Opportunities
- Bridge Overview: The most iconic shots of Donghai Bridge can be captured from elevated viewpoints on either end of the bridge. These vantage points offer sweeping views of the bridge stretching across the sea, showcasing its impressive length and engineering. Early morning or late afternoon light can create dramatic shadows and reflections on the water.
- Seascape Views: Along the bridge, there are opportunities to capture stunning seascape photographs. The contrast between the modern structure and the natural seascape creates compelling compositions. During sunset or sunrise, the interplay of light on the water and the bridge structure can result in breathtaking images.
- Port Activity: Near the Yangshan Deep-Water Port end of the bridge, photographers can capture images of large container ships passing under the bridge or docking at the port. These shots can convey the scale and importance of the bridge in international trade.
- Architectural Details: Close-up shots of the bridge’s structural elements, such as the cable stays, pillars, or the road surface, can provide interesting abstract compositions and highlight the engineering aspects of the bridge.
Modern Importance
- Economic Impact: Donghai Bridge plays a crucial role in China’s economy by connecting Shanghai to the Yangshan Deep-Water Port. This connection has significantly boosted Shanghai’s shipping capacity, allowing it to handle larger container ships and increasing its competitiveness as a global port. The bridge has contributed to the growth of trade and commerce in the region, supporting China’s position as a major player in international trade.
- Technological Showcase: The bridge serves as a demonstration of China’s engineering capabilities and technological advancement. Its construction involved overcoming significant challenges posed by the marine environment, and the techniques and technologies developed during its construction have been applied to other large-scale infrastructure projects in China and around the world.
- Transportation Efficiency: By providing a direct road link to the Yangshan Deep-Water Port, Donghai Bridge has greatly improved transportation efficiency. It has reduced travel times for goods and people moving between the mainland and the port, contributing to the overall efficiency of Shanghai’s logistics network.
- Environmental Considerations: The bridge’s design and construction incorporated various environmental protection measures. For example, efforts were made to minimize the impact on marine life during construction, and the bridge’s elevated design allows for the free flow of ocean currents. These aspects highlight the growing importance of balancing infrastructure development with environmental protection in modern China.

FAQ
- What is Donghai Bridge famous for?
Donghai Bridge is famous for being one of the longest cross-sea bridges in the world, connecting Shanghai to the Yangshan Deep-Water Port and playing a crucial role in China’s maritime trade. - What’s inside Donghai Bridge?
Donghai Bridge is primarily a six-lane expressway. While you can’t go inside the bridge structure itself, you can drive across it and observe its impressive engineering features. - Is Donghai Bridge free?
There is no pedestrian access or entrance fee for Donghai Bridge. However, vehicles using the bridge may be subject to standard road tolls. - Is Donghai Bridge worth visiting?
While Donghai Bridge is primarily a functional structure, it can be worth visiting for those interested in engineering marvels or to experience the impressive views of the East China Sea. - What to do in Donghai Bridge?
The main activity on Donghai Bridge is driving across it. However, you can also appreciate the views of the sea and observe the engineering of the bridge during your journey. - How do I get to Donghai Bridge in the local city?
From Shanghai, you can reach Donghai Bridge by taking the S2 Expressway towards the Yangshan Deep-Water Port. There are also long-distance buses from Shanghai to Yangshan Port that use the bridge. - How to visit Donghai Bridge?
The best way to visit Donghai Bridge is by car or bus. You can drive across the bridge as part of a trip to Yangshan Deep-Water Port, or take a long-distance bus that uses the bridge route.